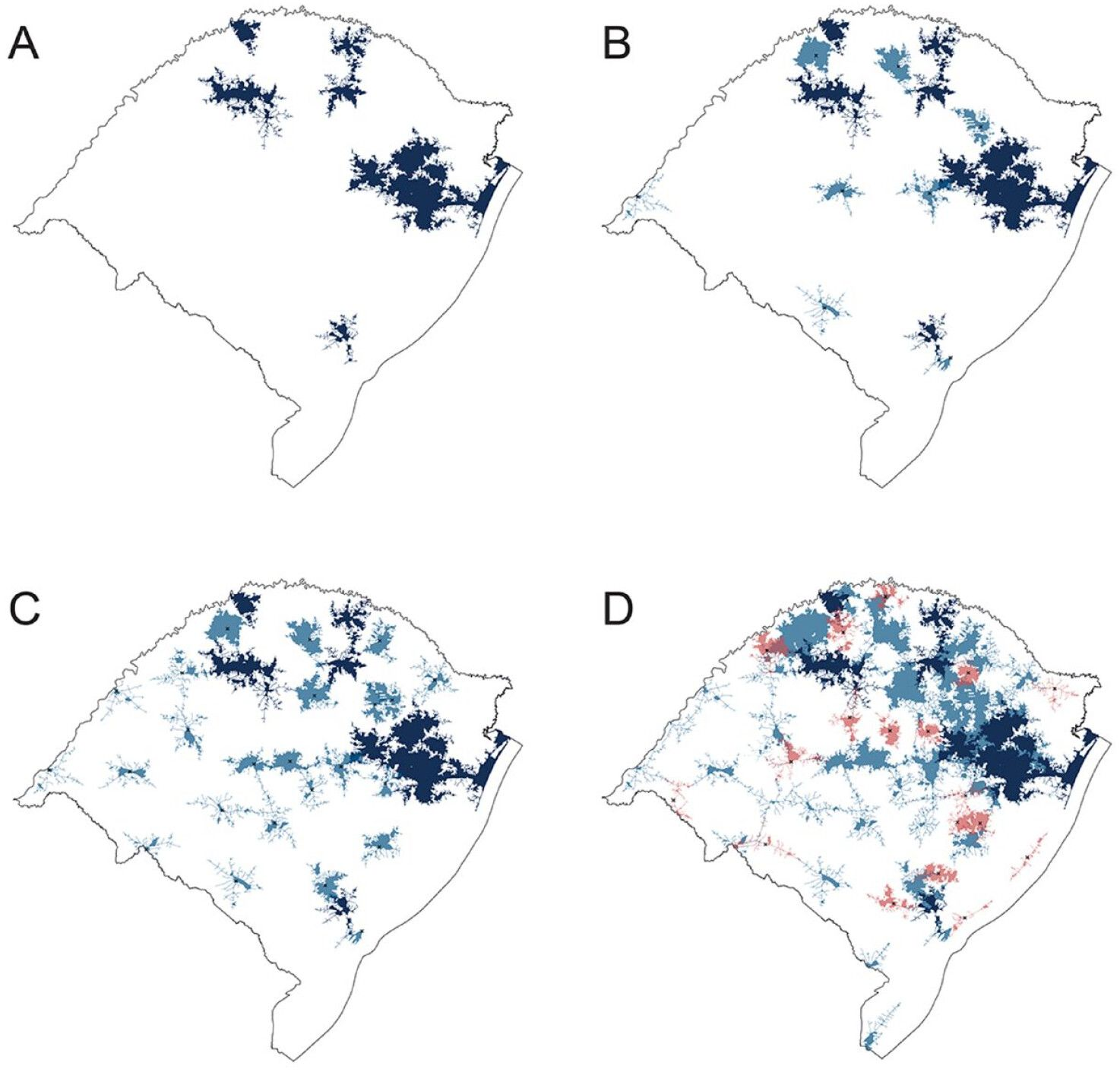
Global access to acute stroke treatment is variable worldwide, with notable gaps in low and middle-income countries (LMIC), especially in rural areas. Ensuring a standardized method for pinpointing the existing regional coverage and proposing potential sites for new stroke centers is essential to change this scenario. This project aim to create and apply computational strategies (CS) to determine optimal locations for new Acute Stroke Centers (ASCs), with a...
Read More
The laboratory of Structural Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
conducts research in data science, machine learning, optimization/meta-heuristics,
and high-performance computing for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology.
Projects developed in the laboratory cover sectors of Agricultural Biotech;
Animal Biotech; Industrial Biotech; Medical Biotech; and Forensic Biotech.
The group is engaged in the following scientific-technical
projects:
Traceability of Cannabis sativa L. in Brazilian Territory
Cannabis sativa L. (Cannabaceae) is a flowering herb that has been domesticated and has agronomic value as a source of food, fiber, and medicine. In its chemical composition, the most prominent molecules found are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabinol (CBD), with THC having psychotropic activity and used for recreational and spiritual purposes for millennia. On the other hand, the genomic analysis of the plant, allowed the identification of hundreds to millions of different markers, using short repetitive sequences (SSR) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)...
Read More
Contribution of swine waste treatment processes in
the control of antimicrobial resistance transmission for
agropastoral systems
The problem of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is recognized within the scope of human health, animal health, and the environment (One Health). It is believed that the highest circulation of resistant bacteria occurs in the environment, released into the environment along with human and agro-industrial waste. As a result, combating AMR has become a priority in all forums of discussion among nations, and goals and actions have been agreed upon by decision-making authorities. Brazil, as a member of the World Health Organization (WHO), has developed the National Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Antimicrobial Resistance in the context of One Health (PAN-BR) in cooperation between the Ministry of Health and the...
Read More
Data Science for Biotechnology Applications: solving large-scale
challenges using explainable machine learning, metaheuristics, and
high-performance computing
This project aims to develop new bioinformatics tools based on Machine Learning methods (supervised and unsupervised), heuristic search methods, and high-performance computing to explore high-dimensional data in problems of scientific and economic interest in the area of human and animal health. We will develop: (i) algorithms based on adaptive and multiobjective metaheuristics; (ii) multimodal metaheuristics; (iii) time series-based metaheuristics; (iv) combinatorial optimization; (v) interpretable machine learning methods; (vi) algorithms for feature extraction and selection; and (vii) combination of interpretability methods aiming at building general-purpose strategies that contribute to the analysis of large data with complex structure...
Read More
Interpretability and Multi-Objective
Heuristic Search Methods for Feature
Selection on High-Dimensional Data
This project aims at developing new approaches that enable the extraction of implicit and hidden knowledge from the vast amount of data existing in different application domains, particularly in problems explored in the field of Bioinformatics. This will allow us to better understand the functional and structural aspects of genes, proteins, and their relationships with pathological phenotypes, for example. Machine learning techniques can efficiently handle non-linear and noisy environments and appropriately handle missing data. However, the predictive model induced by machine learning algorithms is not always easily interpretable. Interpretable machine learning is the collection of algorithms and techniques that enable humans to understand the reasons behind a decision made by a machine learning model. The completion of this research project...
Read More
AICaBI: Artificial Intelligence for Cancer Biomarkes Identification
The current scenario is characterized by a technical capacity to produce large-scale data that goes beyond our analytical capacity for interpretation. The comprehensive characterization of genomic, epigenomic, transcriptomic and proteomic alterations in pathological states, especially when correlated with clinical characteristics, has a great potential to improve the diagnosis and prognosis of diseases, and especially, to enable the practice of personalized medicine in the reality of care activities. This project comprises four big areas: Computational Sciences, Molecular Biology, Bioinformatics and Health Sciences. The aim of this project is to contribute to the personalized medicine...
Read More
Mesoscopic Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Development of
Models and Computational Strategies for Complex Structural
Bioinformatics Problems
There is a wide range of unanswered scientific questions which cannot be answered neither by experiments nor by classical modeling and simulation approaches. One question is how to consider microscopic and macroscopic effects in one model. On the one hand, available microscopic approaches (Molecular Dynamics (MD) type) are precise but computational too complex for large or multi-scale problems. On the other hand, several macroscopic methods (Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) type) cannot show crucial microscopic effects. Therefore, a mesoscopic scale model is required that closes this gap. For such a Mesoscopic Molecular Dynamics (MMD) model, we propose to take advantage of...
Read More
Parallel and Distributed Metaheuristics for Structural Bioinformatics
Structural bioinformatics deals with problems where the rules that govern the biochemical processes and relations are partially known which makes hard to design efficient computational strategies for these problems. There is a wide range of unanswered questions, which cannot be answered neither by experiments nor by classical modeling and simulation approaches. Specifically, there are several problems that still do not have a computational method that can guarantee a minimum quality of solution. The general goal of this project is to develop metaheuristics models based on robust and scalable parallel and distributed computing for structural bioinformatic problems. International Project...
Read More
Multi-modal and multi-objective heuristic search methods for Structural Bioinformatics
problems
In Structural Bioinformatics, several problems do not present a computational method that can guarantee the minimum quality of their solutions. Structural bioinformatics deals with problems where the rules governing biochemical processes and their relationships are partially known, making it challenging to develop efficient computational strategies. Among these problems, two are the most challenging: predicting the three-dimensional structure of macromolecules and the molecular docking problem. Predicting the structure of a polypeptide/protein just from its linear sequence of amino acid residues represents a challenging problem in the field of mathematical optimization, being classified...
Read More